The listener supports no services
Let's see the current status of listener.
[oracle@primary01 ~]$ lsnrctl status
...
Listener Log File /u01/app/oracle/diag/tnslsnr/primary01/listener/alert/log.xml
Listening Endpoints Summary...
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=primary01)(PORT=1522)))
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=ipc)(KEY=EXTPROC1522)))
The listener supports no services
The command completed successfully
Apparently, the listener is running, but it has no service name registered with it. Another point is, using a non-default port like to listen connections needs more configuration skill than normal.
For database users, even though the listener is up and running, they may receive ORA-12514 in their connection tools. I talked about some causes and solutions to ORA-12514 in another post.
By the way, the formal error code of "The listener supports no services" is TNS-01030.

Rationale
In most cases, the message indicates that the database instance is closed, no any database services are available. You can just startup your database and make sure the service names are correct.
If the database is online and you don't see any services registered with the listener, then we should find out what happened.
To know what's the problem depends on what you saw in LOCAL_LISTENER.
Explicit Address
If you're pretty sure that your database instance is up and running, please check the parameter of local listener.
SQL> show parameter local_listener
NAME TYPE VALUE
------------------------------------ ----------- ------------------------------
local_listener string (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=
192.168.0.11)(PORT=1521))
Although we use a non-default port, i.e. 1522 in this case to listen connections, the LOCAL_LISTENER points to the default port 1521.
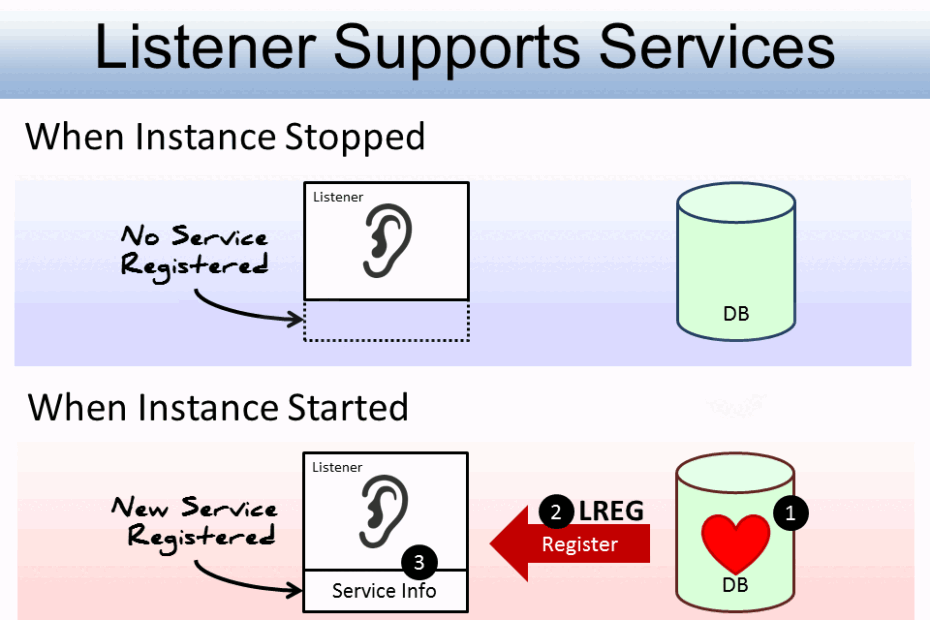
Normally, we don't have to set LOCAL_LISTENER parameter explicitly, because the database instance will look for an existing and appropriate local listener to register its services after startup. Once the listener accepts dynamic service registration, it facilitates connections to get database service subsequently.
Let's continue reading this post to see how we register the service in the listener.
Alias Name
For 12c and later releases, like 19c, you might see an alias name set for LOCAL_LISTENER.
SQL> show parameter local_listener
NAME TYPE VALUE
------------------------------------ ----------- ------------------------------
local_listener string LISTENER_ORCL
That's because the alias name has been used for setting LOCAL_LISTENER, we should check tnsnames.ora, the alias management system for sure.
Solution
To solve the problem depends on what you saw in LOCAL_LISTENER.
Explicit Address
In this case, we want it go to port 1522. Apparently, it went to the wrong port. Therefore, we corrected the setting by this:
SQL> alter system set local_listener='(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=192.168.0.11)(PORT=1522))';
System altered.
SQL> show parameter local_listener
NAME TYPE VALUE
------------------------------------ ----------- ------------------------------
local_listener string (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=1
92.168.0.11)(PORT=1522))
Please note that, if the instance was startup with a SPFILE, it implied SCOPE=BOTH in the above statement. Otherwise, it implied SCOPE=MEMORY.
After setting the parameter, a background process called listener registration (LREG) will discover the target listener in 60 seconds and send information such as the service name, instance names, and workload information to the listeners. Therefore, you don't have to register it by yourself.
Of course, you can override the 60-second delay of LREG by this SQL statement below:
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM REGISTER;
The above statement forces LREG to register with the listener in order to support the database service immediately.
After registration, the listener starts to deal with connections that are meant for the database. Service handlers, either dispatchers or dedicated server processes, will be used to maintain the connections. Once the connections between clients and database established, the listener stepped aside and continued to listen to new connections.
Multiple Listeners
By the way, as for multiple listeners, you can do this:
SQL> alter system set local_listener='(ADDRESS_LIST=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=192.168.0.11)(PORT=1521))(ADDRESS= PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=192.168.0.12)(PORT=1521)))';
We can use ADDRESS_LIST to accommodate more listeners than one in the above.
Will it show The listener supports no services this time? Let's check the listener again.
[oracle@primary01 admin]$ lsnrctl status
...
Listener Log File /u01/app/oracle/diag/tnslsnr/primary01/listener/alert/log.xml
Listening Endpoints Summary...
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=primary01)(PORT=1522)))
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=ipc)(KEY=EXTPROC1522)))
Services Summary...
Service "ORCL" has 1 instance(s).
Instance "ORCL", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service...
Service "ORCLXDB" has 1 instance(s).
Instance "ORCL", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service...
The command completed successfully
It's back. The listener is holding the services now.
By the way, the service name is usually the same as DB_UNIQUE_NAME in a RAC environment by default. For a single-instance database, the service name is usually the instance name, i.e. $ORACLE_SID.
Alias Name
If LOCAL_LISTENER is using an alias to manage the listener destination, then it implies we should look for the entry in tnsnames.ora.
[oracle@test ~]$ vi $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/tnsnames.ora
...
LISTENER_ORCLX =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = test.example.com)(PORT = 1521))
As you can see, they are mismatched with each other, one is LISTENER_ORCL, the other is LISTENER_ORCLX. In such case, you should either modify LOCAL_LISTENER or this entry, whichever depends on your judgement.
Correct LOCAL_LISTENER
SQL> alter system set local_listener='LISTENER_ORCLX';
System altered.
SQL> show parameter local_listener
NAME TYPE VALUE
------------------------------------ ----------- ------------------------------
local_listener string LISTENER_ORCLX
Correct Alias Name
[oracle@test ~]$ vi $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/tnsnames.ora
...
LISTENER_ORCL =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = test.example.com)(PORT = 1521))
We should re-altering the parameter to make the database system refresh its underlying connection string cache.
SQL> alter system set local_listener='LISTENER_ORCL' scope=memory;
System altered.
Static Services
Whereas dynamic services have to be registered with the listener only when the database is up and running, static service registration can be done very early when the listener startup, no matter the database instance does exist or not.
That is to say, static services in listener don't care about the database instance. You can connect to an idle database as SYS from any remote clients via static services in order to maintain the database. This can be a workaround to The listener supports no services. Because there already have services upheld by the listener.
The common jobs that need to connect an idle or nomount database, for examples, could be starting up a database remotely or duplicating an auxiliary database, say a standby database from a target database.
To take advantages of static service registration, you have to add an entry called SID_LIST_LISTENER to the configuration file of listener, which is usually at $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/listener.ora. Static services will take effect after you restart the listener.
More Considerations
Whenever in doubt, use tnsping and then sqlplus to test all situations of listener or service problems.
If you still have troubles on adding a new listener to a grid infrastructure (RAC), you can refer to my tutorials as below:
- How to Add a Cluster Listener on Default Network to Grid
- How to Add a Cluster Listener on Second Network to Grid
They might give you some clues to solve The listener supports no services from different angles.
Thanks helped me after long search
It’s my pleasure.
Excelent post, thanks helped me!
My pleasure!
Thanks, really helpful and well written article.
You’re welcome, I’m glad it’s helpful.
thanks helped me after a server recovery.
You’re welcome.
Hi,
this was an EXCELLENT Tipp! I restored my machine from a VM Ware snapshot and for what reason ever the listener was not supporting my service anymore! But with this tipp it is working now again!
THANK YOU!!
Best regards
Winnie
It’s my pleasure!
Thank you, excellent post!
You’re welcome!
Excellent Post, It resolved my issue.
It’s my pleasure.
Simple and Clearly !
Thanks !
It’s my pleasure.
Thank u very much, this post solved my issue. Well , I come from China.
You’re welcome! Alan.
Hi
Very helpful. My issue related to “listener supports no services” got resolved.
Thank you. very informative post.
You’re welcome! Very happy to hear that.
THANK YOU SO VERY MUCH!!!
It’s my pleasure.
Very Helpful!
Thank You Mr. Chen.
I’m glad it’s helpful.
Thanks a lot…….greatly helps me to solve my issue
My pleasure!
very useful tip. Thanks!
My pleasure!
Muchas gracias me sirvió bastante
De nada!
Hi,
Thank you!
Really it’s helpful.
Regards,
Mohammed Thaseen
I’m so glad I could help.
I installed oracle restart 19c for a client and inspite of everything running fine, the service was registering with the listener. This article helped me resolved the issue by setting the local listener correctly. Thank you very very much.
Thanks for sharing your experience.
Great article and helped resolve the problem, but whenever listener is restarted, again the service is not registered. Should one use what you call Static Services defined in listener.ora
Yes, the static service is the last resort.
Hi,
I tried the following that you mentioned in the post. Its not working for me.
Given below are the listener.ora and tnsnames.ora. I am using 19c.
Thanks in advance for your help.
This is the error i am getting.
TNS-12541: TNS:no listener
TNS-12560: TNS:protocol adapter error
TNS-00511: No listener
Linux Error: 111: Connection refused
listener.ora
LISTENER =
(DESCRIPTION_LIST =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = ol7-orcl193.localdomain)(PORT = 1521))
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = IPC)(KEY = EXTPROC1522))
)
)
tnsnames.ora
ORCL19C =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = ol7-orcl193)(PORT = 1521))
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVER = DEDICATED)
(SERVICE_NAME = orcl19c)
)
)
ORCL19C_PDB =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = ol7-orcl193.localdomain)(PORT = 1521))
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = IPC)(KEY = EXTPROC1522))
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVER = DEDICATED)
(SERVICE_NAME = ORCL19C_PDB)
)
)
Obviously, the destination that you want to reach has no listener service. That’s why you saw TNS-12541: TNS:no listener.