In this post, I will introduce the expanding steps for both Windows and Linux guest VMs. The first 4 steps A. B. C. D. are the same, but step E. is a lot differences between the two platforms.
Please notice that VMware virtual disks are expandable only when they were chosen as "persistent" from the beginning which is set up in configuration time.
A. Power off all guest VMs
You can't expand the virtual disks online.
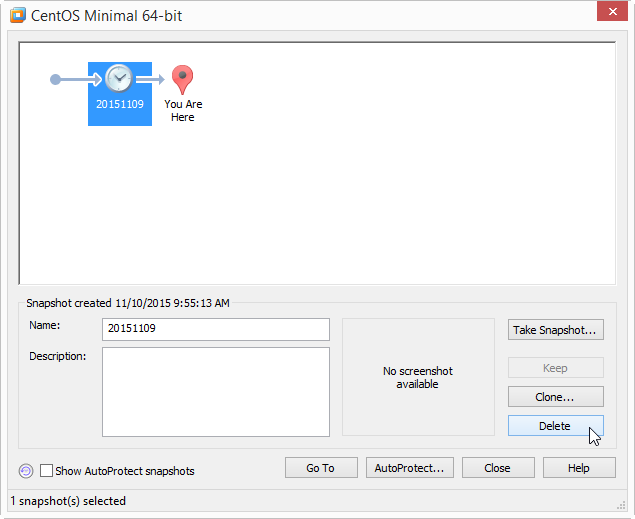
B. Delete all snapshots on guest VMs.
This is a required step, if you want to keep all snapshots in the VM, I suggest that you clone a new VM for the disk expansion.
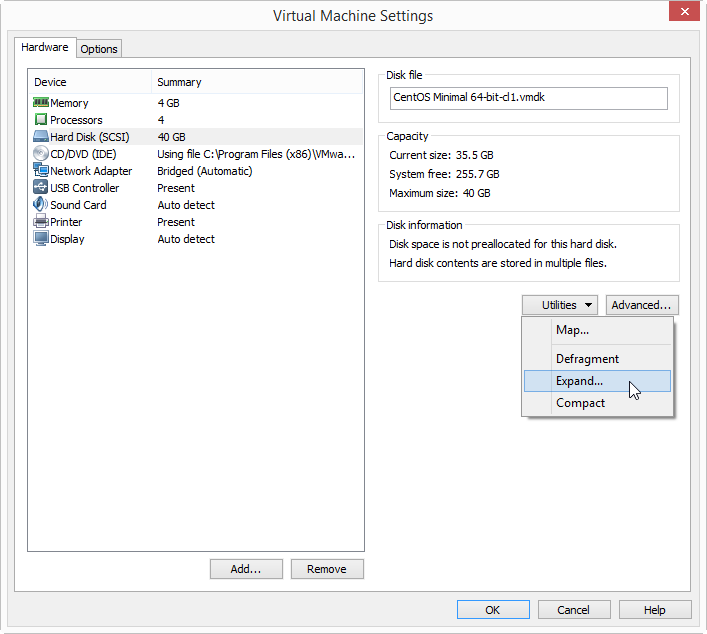
C. Expand the virtual disk by VMware untilities.
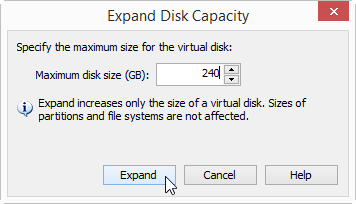
D. Power on all guest VMs.
So far, we have expand the virtual disk space, but we have to power on the guest OS in order to expand the disk space on OS-level in the next step.
E. Extend the disk space in guest OS.
There're two main kinds of platform that you might be in, which are Linux and Windows respectively.
Kindly suggest you that, taking a snapshot in order to prevent the guest OS from accidental corruptions before expanding the space. Let's see how we do it in these platforms.
In Linux VM:
It's more complicated to expand the space on Linux than Windows, I use two major steps to achieve our goal. Please feel free to follow my other posts below:
- Step 1: How to Increase Volume Group Size on Linux
- Step 2: How to Increase Logical Volume Size on Linux
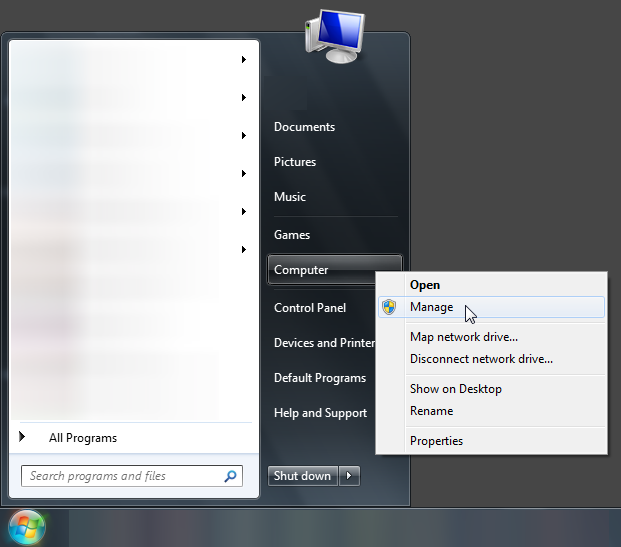
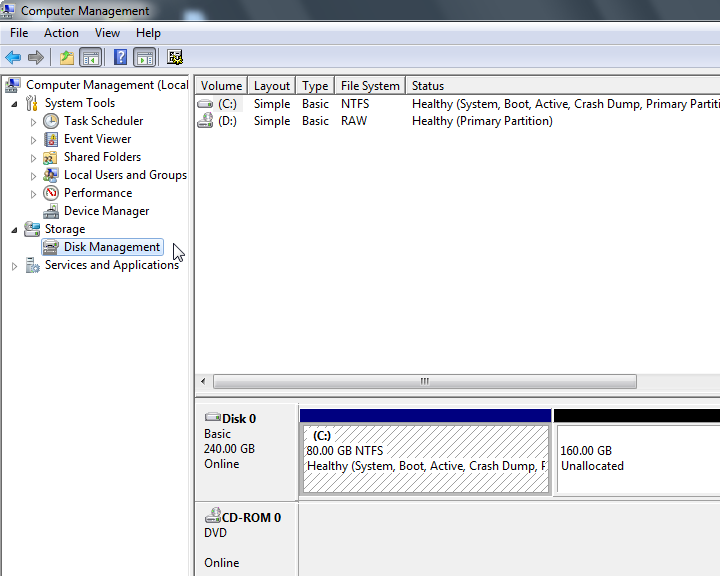
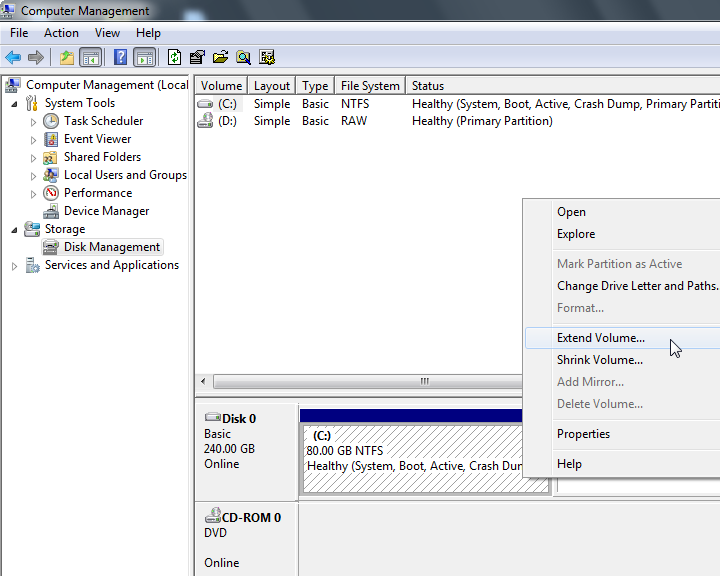
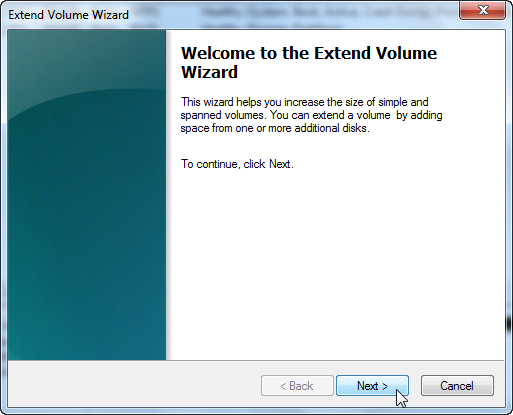
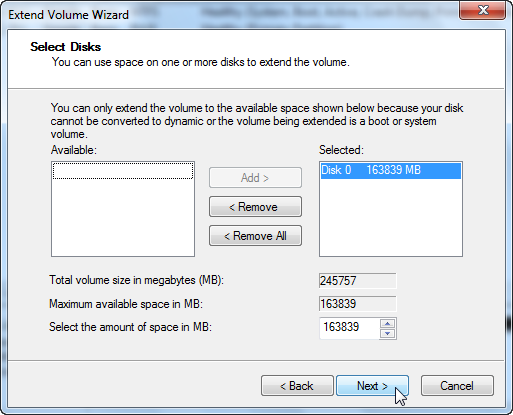
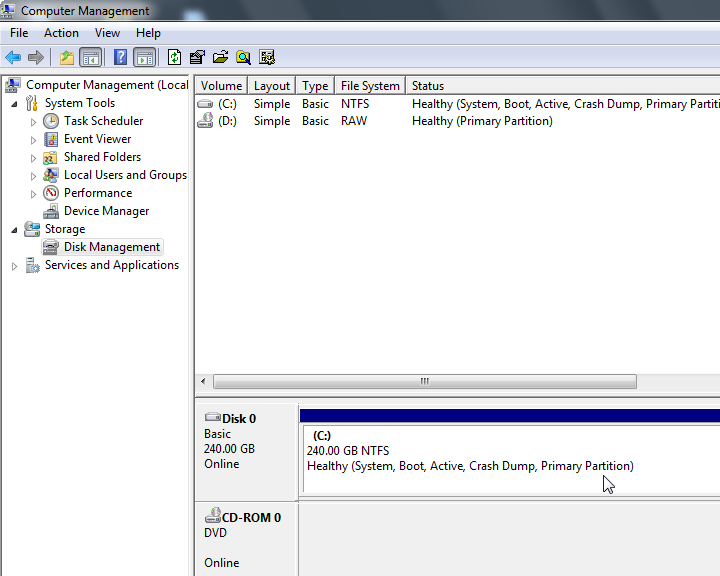
In Windows VM:
Windows has a nice disk management tool to expand the space.