Usually, we copy, paste and modify the block of a TNS entry in tnsnames.ora to create a new net service name for local naming.
For normal users who don't know how to manipulate tnsnames.ora, they can also add a new net service name by Net Configuration Assistant (NETCA).
In this post, we will introduce the way to create a new net service name by NETCA.
Windows
For windows platform, you may launch NETCA by clicking it on the menu.
Linux
For Linux or Unix platform, you may issue netca to launch it.
[oracle@test ~]$ netca
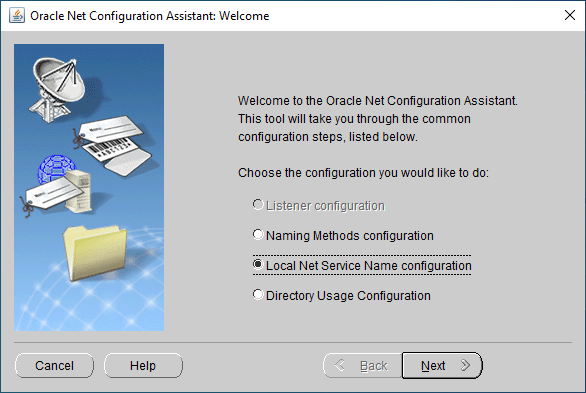
We choose "Local Net Service Name configuration".
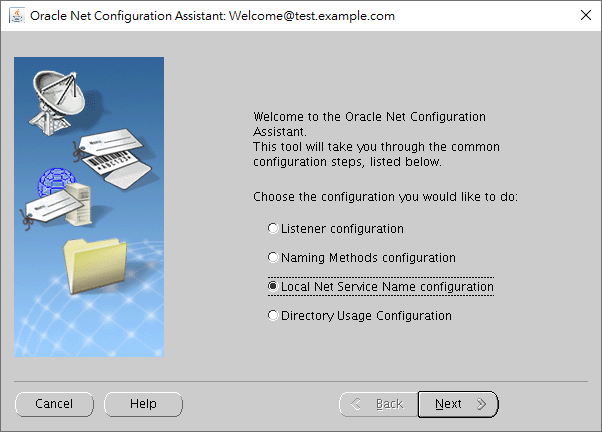
As you can see, the first item has been disabled for client edition. For server edition, you may see more items like this:
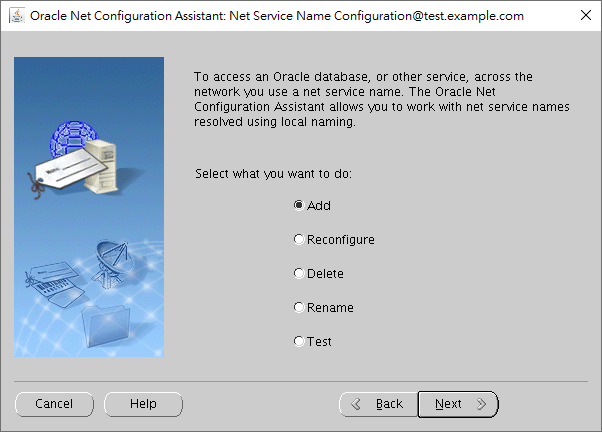
In this case, we take the server edition for an example to reach our goal.
We would like to add a net service name.
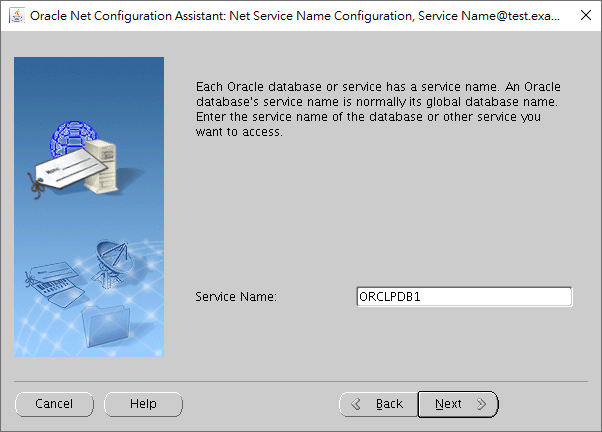
We input the specific service name of a database, which is a name registered in the listener to receive connections from clients. If you don't know the database service name, you may ask your DBA for an answer.
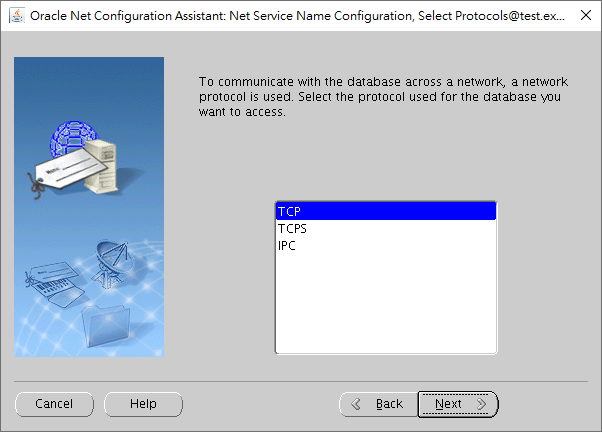
TCP only would be fine.
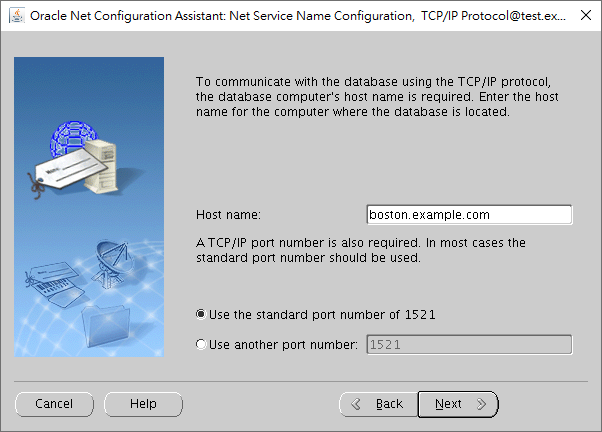
You have to input the destination of the database server.
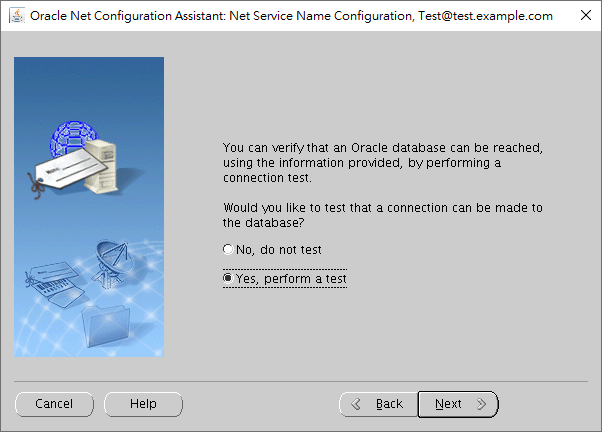
If you want to perform a connection test, you may choose it now.
Here we click the button of "Change Login".
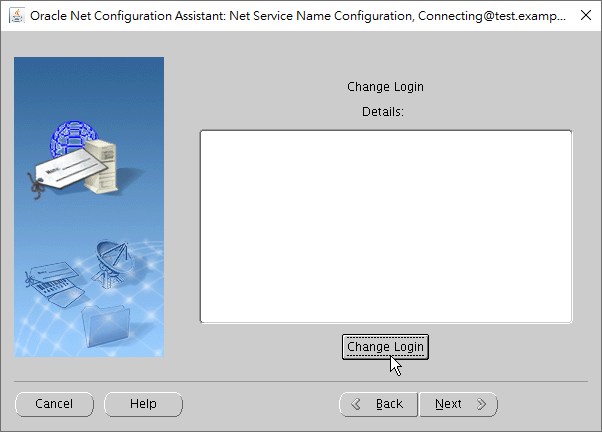
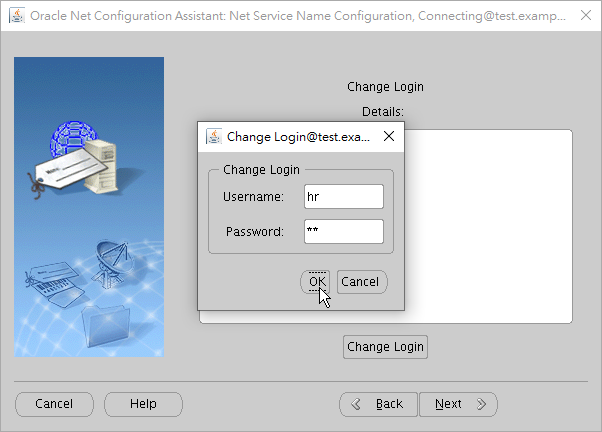
Then input the user's credentials including username and password.
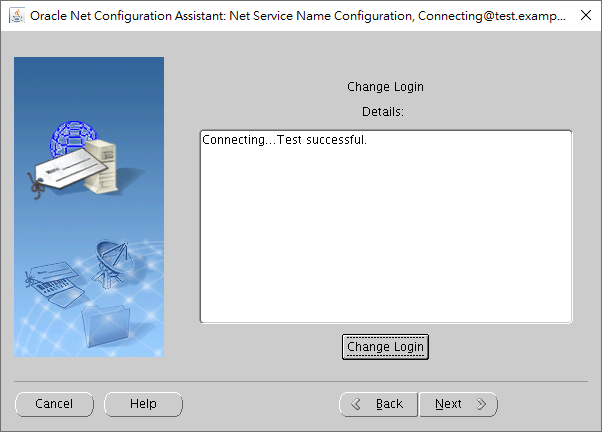
As you can see, the connection test is successful.
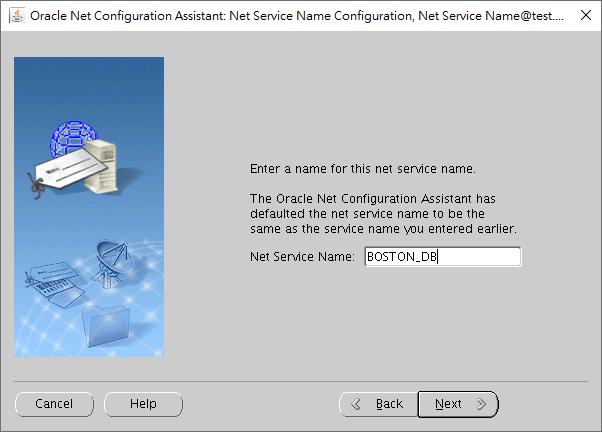
We input a new TNS name to be resolved by the configuration file tnsnames.ora of local naming.
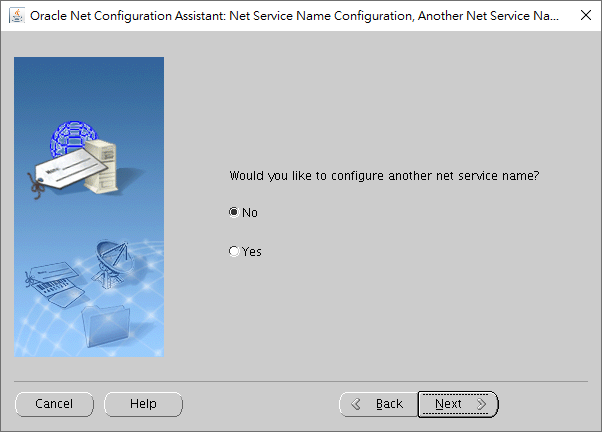
If you have another TNS name needs to be created, you may click "Yes", otherwise, click "No".
The page notifies us that the new TNS name has been added.
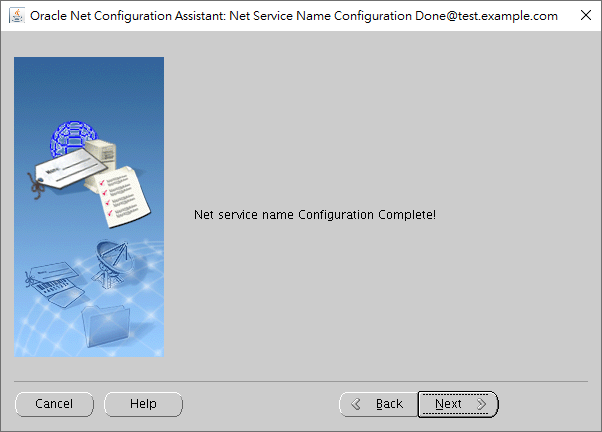
We click on "Finish" to exit NETCA.
The output of NETCA would look like this:
[oracle@test ~]$ netca
Oracle Net Services Configuration:
Default local naming configuration complete.
Created net service name: BOSTON_DB
Oracle Net Services configuration successful. The exit code is 0
To trace back the process, you may check the log of NETCA.
To see the result, you may display the file if you know the location of tnsnames.ora.
For Linux OS, you can do this:
[oracle@test ~]$ cat $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/tnsnames.ora
...
BOSTON_DB =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS_LIST =
(ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = boston.example.com)(PORT = 1521))
)
(CONNECT_DATA =
(SERVICE_NAME = ORCLPDB1)
)
)
Its looks good.